Current Research Projects


Next Generation Smart (Macro)molecular Antimicrobial Prodrugs
This is a recent flagship programme based on Edgar's awarded ARC Future Fellowship grant. The idea is to impart intelligence to antimicrobial (macro)molecules where the activity can be activated only in the presence of a stimuli such as light or bacteria (enzymes). This prodrug strategy is envisioned to improve biocompatibility and reduce toxicity issues that is essential towards clinical translation. Relevant papers from this programme include:
i) Chem. Sci., 2025, DOI: 10.1039/D5SC02412A
ii) Polym. Chem., 2025, 16, 1373.

Reviving 'Resisted' Traditional Antibiotics with (Macro)molecular Antimicrobials
Commercial antibiotics that are no longer susceptible to drug-resistant bacteria could be revived in the presence of membrane-active antimicrobial molecules via combination therapy. This is an important programme aimed at developing and understanding new combination strategies to combat drug-resistant bacteria as well as to preserve the use and lifespan of current antibiotics. Relevant papers from this programme include:
i) Biomacromolecules, 2024, 25, 6899
ii) ACS Infect. Dis., 2022, 8, 1480
iii) ACS Infect. Dis., 2021, 7, 215 - review article

Smart Membrane-Disrupting (Macro)molecular Anticancer Agents
This is a new sister programme to the biologically responsive antimicrobials programme above. The technology here revolves around the same concept of smart activation targeted for anticancer applications, with the same overall goal of reducing the toxicity of the anticancer agents. Work is currently in progress to develop the first platform system. Stay tuned!
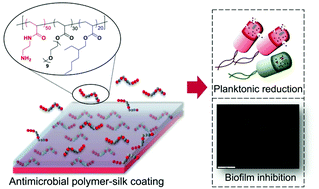
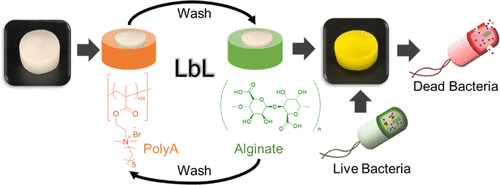
Antimicrobial Coatings and Materials for Fighting 'Superbugs'
This programme focuses on the development of coatings and materials that are capable of combating multidrug-resistant bacteria, specifically for applications in biomedical devices, textiles, wound dressing materials and water disinfection technologies. Strategies range from using non-leaching antimicrobial polymers to releasable nitric oxide and iodine molecules. Relevant papers from this programme include:
i) Appl. Surf. Sci., 2023, 641, 158422
ii) Polym. Chem., 2021, 12, 7038
iii) ACS Appl. Bio Mater., 2021, 4, 692